

Hidroeléctrica de Cahora Bassa
HCB
Hidroeléctrica de Cahora Bassa, SARL (HCB): Mozambique's Hydropower Giant
Hidroeléctrica de Cahora Bassa, SARL (HCB) is Mozambique's premier hydropower company, operating the Cahora Bassa Hydroelectric Power Station on the Zambezi River in Tete Province. Established as a cornerstone of the country's energy sector, HCB is the largest independent power producer (IPP) in Southern Africa, supplying the majority of Mozambique's electricity and exporting power to neighboring countries via the Southern African Power Pool (SAPP).
History and Ownership
-
Founding: HCB was formally established on June 24, 1975, during Mozambique's transition to independence, following a protocol between the Portuguese government and the Mozambique Liberation Front (FRELIMO). Construction began in 1969, with the reservoir filling starting in December 1974 and the power station progressively coming online from 1977.
-
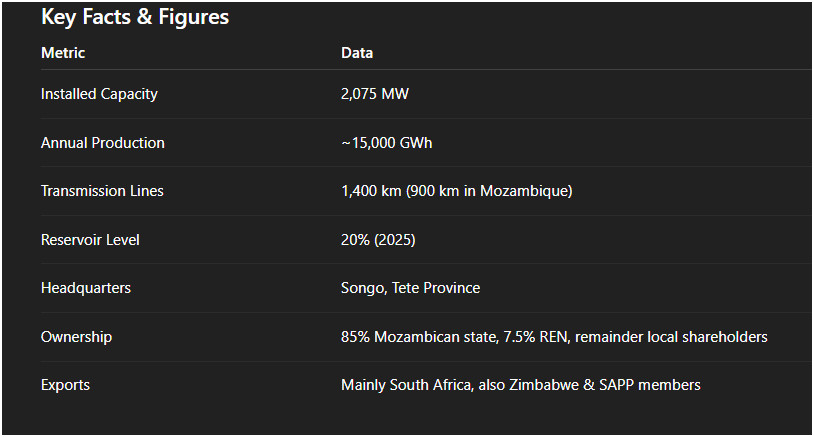
Ownership Evolution: Initially, Portugal held 82% of HCB, with Mozambique at 18%. In 2007, Mozambique gained majority control (85%), while Portugal retained 15% through Redes Energéticas Nacionais (REN). Remaining shares are distributed among Mozambican citizens, companies, institutions, and HCB itself.
-
Headquarters: Songo, Cahora Bassa District, Tete Province, Mozambique.
Dam and Infrastructure
-
Dam Specifications: The Cahora Bassa Dam is an arch dam standing 171 meters high and 303 meters wide, creating Lake Cahora Bassa, Africa's fourth-largest artificial lake, stretching 240 km westward.
-
Power Station: HCB has five 415-MW generator sets, totaling 2,075 MW, making it one of Africa's largest hydropower plants.
-
Transmission Infrastructure: Connected via a 533 kV bipolar HVDC line to converter stations in Songo (Mozambique) and Apollo (South Africa), spanning 1,400 km with about 4,200 towers in Mozambique. The line supports exports to South Africa, Zimbabwe, and other SAPP members.
Energy Production
-
Annual Output: Designed for 13,100–15,000 GWh, actual production varies with water levels. In 2021, production reached 10,899.79 GWh, slightly below 2020 levels due to drought.
-
Capacity Utilization: Supplies over half of Mozambique's electricity needs, with ~90% historically exported to support industrial demand such as the Mozal Aluminium Smelter.
-
Recent Challenges: As of 2025, the reservoir is only 20% full due to prolonged drought, threatening output reductions.
Economic and Financial Contributions
-
Between 2007–2014, HCB generated 115 billion meticais (~US$1.8 billion).
-
From 2022–2024, it contributed over US$362 million in taxes and US$152 million in concession fees, representing 37% of contributions over 17 years.
-
HCB distributed dividends in 2023 for the 2022 fiscal year and launched a public offering in October 2024, selling 2.5% of its capital (~680 million shares) on the Bolsa de Valores de Moçambique.
Recent Projects and Developments
-
Rehabilitation & Modernization: HCB secured a US$125 million loan in 2022 and awarded a multi-million-euro contract to ANDRITZ in 2025 to refurbish its five generating units, ensuring continued operations while upgrading infrastructure.
-
Expansion – Cahora Bassa North: A planned 1,250 MW hydropower project, slated to begin construction in 2028 and operate commercially by 2032, expected to generate 2,983 GWh annually. State Grid Corporation of China holds a 7.5% stake in this project.
-
Sustainability: HCB emphasizes environmental and social responsibility, supporting community programs in Songo and Tete while aligning with Mozambique's national energy strategy.
Strategic Importance
HCB is not only the backbone of Mozambique's electricity supply but also a critical contributor to regional energy security. By exporting power to neighboring countries, supporting industrial hubs, and investing in new projects, HCB drives economic growth, creates jobs, and reinforces Mozambique's role in the Southern African Power Pool.
Summary
Hidroeléctrica de Cahora Bassa, SARL remains Mozambique's energy powerhouse, combining history, strategic infrastructure, and ambitious expansion projects to maintain its status as a regional leader in hydropower. Its commitment to sustainable energy and regional integration ensures it will continue to power Mozambique and Southern Africa for decades to come.